Table of Contents

Cloud computing definition
Cloud computing meaning is the usage of hosted services such data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software through the internet . Since the advent of cloud computing, the number of cloud-based IT services and apps has exploded around the globe and is still growing.
Cloud-based storage enables you to save files to a remote database rather than a proprietary hard disc or local storage device. An electronic gadget has access to the data and the software applications needed to run it as long as it has internet access.
For a variety of reasons, including cost savings, enhanced productivity, speed and efficiency, performance, and security, cloud computing is a popular choice for both individuals and corporations.
What is multi-cloud computing?
Multi-cloud computing is a cloud computing approach that involves using multiple cloud computing services or platforms from different vendors simultaneously to achieve specific objectives. In this approach, an organization can distribute its workload across multiple cloud providers, rather than relying on a single cloud service provider.
Multi-cloud computing allows organizations to choose the best cloud service for each specific application or workload, based on factors such as cost, performance, and availability. By using multiple cloud providers, organizations can reduce the risk of vendor lock-in, mitigate the impact of cloud outages, and improve overall reliability and scalability.
To implement multi-cloud computing, organizations typically use a combination of public and private clouds, along with other cloud-based services such as software-as-a-service (SaaS) and platform-as-a-service (PaaS). Additionally, organizations may use cloud management tools to manage their multi-cloud environments and ensure consistent performance and security across all cloud platforms.
How does cloud computing work?
Client devices can access data and cloud applications from distant physical servers, databases, and computers via the internet to explain how cloud computing functions.
Using cloud computing services allows businesses to bypass the upfront costs and complexity of purchasing and maintaining their own IT infrastructure in favour of paying only for the services they actually use.
By offering the same services to a wide range of consumers, cloud computing service companies can gain enormous economies of scale.
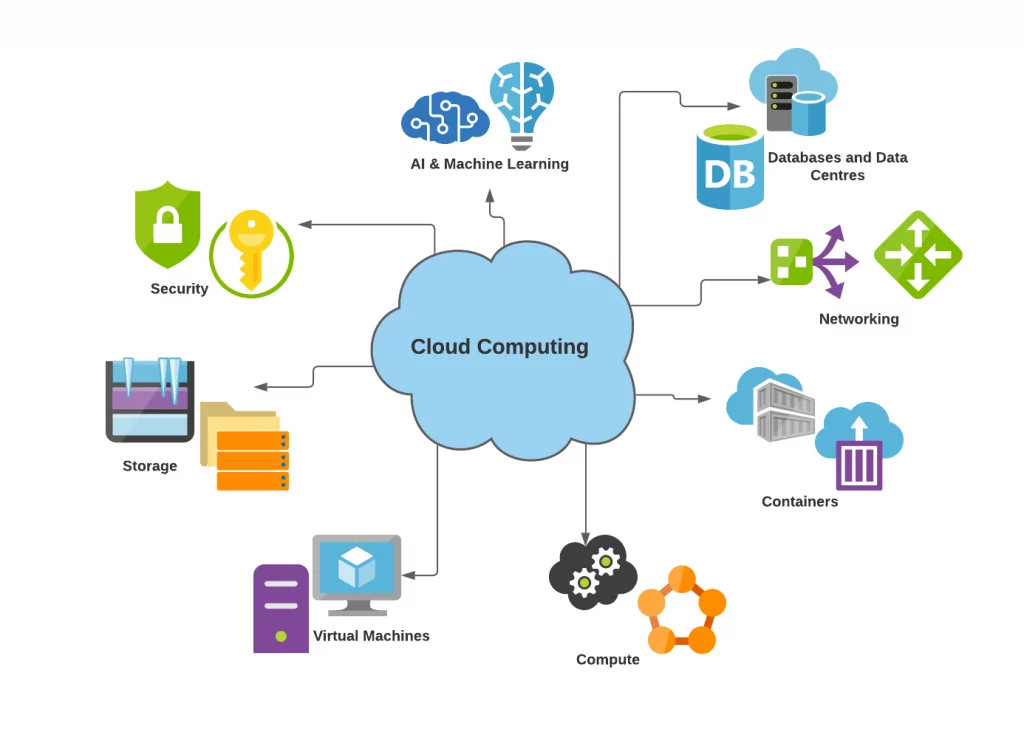
How significant is a cloud?
Cloud computing is a highly significant technology that has revolutionized the way we store, access, and process data. It has transformed the traditional model of on-premise computing by providing an on-demand, scalable, and cost-effective model for accessing computing resources over the internet.
Types of cloud computing
Cloud computing services are a type of service that provides users with access to computing resources, such as servers, storage, applications, and services, over the internet. The resources are provided and managed by third-party providers, which operate and maintain large data centers around the world.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the most basic type of cloud service that provides organizations with virtualized computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and network resources. With IaaS, organizations can provision and manage their own virtual machines, operating systems, and applications on the cloud provider’s infrastructure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides organizations with a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS providers offer pre-configured development environments, application servers, and databases that organizations can use to develop and deploy their applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a complete software application that is delivered over the internet. With SaaS, organizations can use software applications without having to install, manage, or maintain them. Examples of SaaS applications include email, collaboration tools, and customer relationship management software.
Advantages of cloud computing
Cost savings
Cloud computing allows organizations to reduce their capital expenditures on hardware, software, and IT infrastructure. Instead, they can access computing resources on-demand and pay only for what they use.
Scalability
Cloud computing enables organizations to quickly and easily scale up or down their computing resources as their needs change.
Accessibility:
Cloud computing allows users to access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, making it easier for remote teams to collaborate and work together.
Security
Cloud computing providers invest heavily in security measures to protect data from cyber threats, which can be difficult for individual organizations to achieve on their own.
Innovation
Cloud computing providers offer a range of tools and services that allow organizations to innovate and develop new applications and services more quickly and cost-effectively.
Disadvantage of cloud computing
While cloud computing offers many benefits, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
Security concerns:
Cloud computing involves storing and processing data on servers that are owned and managed by third-party providers. This can raise concerns about the security and privacy of data. Organizations may worry about data breaches, unauthorized access, or loss of control over their data.
Dependence on internet connectivity:
Cloud computing services require a reliable and fast internet connection to access and use the cloud-based resources. Organizations that rely heavily on cloud computing can experience downtime or performance issues if they have unreliable or slow internet connectivity.
Potential for vendor lock-in:
Once an organization has invested in a specific cloud provider and has built their applications and systems on that provider’s infrastructure, it can be difficult and expensive to switch to a different provider or to move their applications and systems back on-premise.
Limited control over infrastructure:
With cloud computing, organizations have limited control over the infrastructure and technology stack that their applications and systems run on. This can make it challenging to troubleshoot and resolve issues that may arise.
Costs can add up:
While cloud computing can be cost-effective, costs can add up quickly if organizations are not careful. Some providers charge for every resource used, and there may be additional costs for data transfer, data storage, and other services.
Cloud computing characteristics
On-Demand Self-Service
Cloud computing resources can be easily provisioned and scaled up or down as needed by users, without requiring any manual intervention from the cloud provider.
Broad Network Access
Cloud computing resources can be accessed by users from anywhere in the world with an internet connection, using a variety of devices.
Resource Pooling
Cloud computing resources are shared among multiple users, allowing for efficient and flexible use of computing resources.
Rapid Elasticity
Cloud computing resources can be rapidly scaled up or down to meet changing user demands, without requiring any manual intervention from the cloud provider.
Measured Service
Cloud computing resources are monitored and measured, allowing users to be charged only for the resources they use.
Service Models
Cloud computing offers several service models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Deployment Models
Cloud computing offers several deployment models, including Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, and Multi-Cloud.
Top 10 Cloud Computing Trends for 2023
Multi-cloud environments
Organizations are increasingly using multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in, optimize costs, and improve performance.
Edge computing
Edge computing is becoming more popular as organizations seek to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance.
Hybrid cloud solutions
Hybrid cloud solutions, which combine private and public cloud services, are becoming more common as organizations seek to balance security and control with cost-effectiveness and flexibility.
Serverless computing
Serverless computing is gaining popularity as a way to reduce costs and improve scalability by only paying for the computing resources used when they are used.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Cloud providers are offering more AI and machine learning services to enable organizations to build intelligent applications and automate processes.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is becoming the standard for container orchestration, enabling organizations to deploy and manage containerized applications more efficiently.
DevOps
DevOps practices are becoming more important as organizations seek to automate and streamline their software development processes.
Security
Cloud providers are investing heavily in security to protect data and infrastructure from cyber threats, and organizations are increasingly using cloud-based security solutions.
Cloud-native architecture
Cloud-native architecture, which involves building applications specifically for the cloud, is becoming more popular as organizations seek to take advantage of cloud-specific features and benefits.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Cloud computing is playing an increasingly important role in IoT as organizations seek to process and analyze the large amounts of data generated by connected devices.
What is cloud-computing adoption doing to IT budgets?
Cloud computing adoption is having a significant impact on IT budgets in many organizations. While cloud computing can offer cost savings in the long run, the initial adoption and migration to cloud infrastructure can require a significant upfront investment.
Cloud computing can help reduce capital expenses by eliminating the need to purchase and maintain hardware and software infrastructure. However, the migration to cloud infrastructure often requires a significant upfront investment, which can put pressure on IT budgets.
Operating expenses: Cloud computing can also help reduce operating expenses by enabling organizations to pay for computing resources on a pay-per-use basis. However, ongoing operational expenses such as subscription fees and data transfer costs can add up over time.
Adopting cloud computing may require organizations to train or hire IT staff with cloud computing expertise, which can be expensive. Additionally, organizations may need to invest in training and development programs to ensure their staff can effectively use cloud computing tools.
cloud computing examples in real life
Online Storage
Services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and iCloud use cloud computing to provide users with online storage that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This allows users to store and access their files and data from any device.
E-Commerce
Online shopping platforms like Amazon and eBay use cloud computing to handle the massive amounts of data generated by their websites and to process transactions securely and efficiently.
Social Media
Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram use cloud computing to store and manage the massive amounts of user data generated by their sites.
Streaming Services
Services like Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+ use cloud computing to stream movies and TV shows to users on-demand, without needing to download or store the content locally.
Gaming
Cloud gaming services like Google Stadia and Microsoft xCloud use cloud computing to allow users to stream games over the internet without needing to own powerful gaming hardware.
Healthcare
Cloud computing is used in healthcare to store, manage, and share patient data securely and efficiently. This allows healthcare providers to access patient information from anywhere with an internet connection.
Education
Cloud-based education platforms like Google Classroom and Blackboard use cloud computing to provide online learning resources to students and teachers from anywhere with an internet connection.
Banking
Cloud computing is used in banking to provide secure and reliable online banking services to customers, allowing them to access their accounts and manage their finances from anywhere with an internet connection.
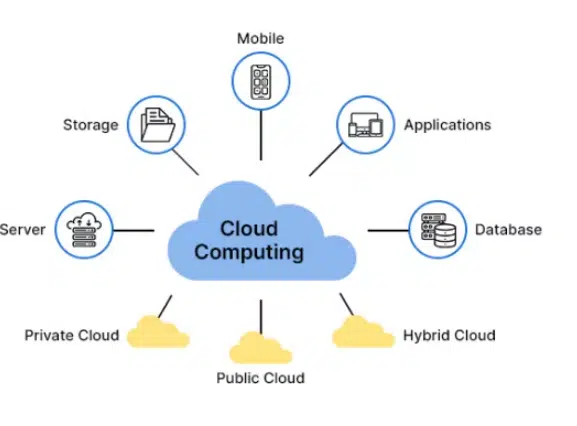
Cloud computing vs virtualization
Virtualization requires the management of virtual machines, including the allocation of resources, while cloud computing typically provides a higher level of abstraction, allowing users to provision and manage resources more easily.Virtualization can be used in cloud computing to provide a flexible and scalable infrastructure, but cloud computing does not necessarily require virtualization.
In summary, virtualization is a technology that enables the creation of virtual resources, while cloud computing is a service delivery model that provides users with access to computing resources over the internet. Virtualization can be used in cloud computing to provide a flexible and scalable infrastructure, but it is not the same thing as cloud computing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud computing has become an essential part of modern technology infrastructure, enabling individuals and organizations to access powerful computing resources over the internet with ease. With its scalable, flexible, and cost-effective nature, cloud computing has transformed the way businesses operate, from startups to large enterprises. As the demand for cloud computing continues to grow, we can expect to see continued innovation and development in this field, as well as increased adoption across a wide range of industries. Overall, cloud computing is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of technology and business, driving innovation, and enabling growth in the digital age.
